Wondering what to do when your smart refrigerator’s touchscreen goes black or your Wi-Fi connected dishwasher suddenly can’t connect to your home network? Let’s dive into the most common smart appliance glitches that leave homeowners scratching their heads, and discover practical solutions you can try before calling in the pros. Picture this: you’re rushing to get dinner ready, and suddenly your smart oven decides it doesn’t want to preheat because it can’t connect to your phone app. Or maybe your voice-controlled dishwasher is giving you the silent treatment, completely ignoring your commands. Welcome to the wonderful world of smart home living, where our appliances are smarter than ever but also more temperamental than a toddler who missed their nap. I learned this lesson the hard way last winter when my smart washing machine decided to have an existential crisis during a power outage. One minute it was happily washing my clothes, and the next it was flashing error codes like it was trying to communicate in Morse code. After spending way too much time on hold with customer service, I discovered that most smart appliance issues can actually be resolved with some basic troubleshooting steps. The key is understanding that these high-tech helpers are essentially computers with washing, cooking, or cooling capabilities, and like any computer, they sometimes need a good restart or software update. Smart appliances have revolutionized our daily routines, offering convenience features like remote monitoring, energy efficiency tracking, and automated scheduling. However, when these advanced features stop working, it can feel like your entire kitchen has gone rogue. The good news is that most smart appliance problems fall into predictable categories, and many can be fixed without requiring professional repair services.
Key Outtakes:
- Most smart appliance connectivity issues stem from Wi-Fi network problems or outdated firmware, not hardware failures
- Power cycling your smart appliances can resolve up to 70% of common technical glitches and software conflicts
- App-related problems often require checking for updates on both your mobile device and the appliance’s internal software
- Smart home integration failures typically occur when devices lose their connection to your home’s hub or voice assistant
- Professional repair services specializing in smart appliances can diagnose complex issues that basic troubleshooting can’t resolve

Understanding Smart Appliance Technology Failures
 Smart appliances are essentially traditional household devices equipped with sensors, processors, and internet connectivity that allow them to communicate with your smartphone, voice assistants, and other connected devices. When these high-tech features malfunction, it’s usually because one of these technological components has encountered a problem rather than the core appliance function failing. Think of it like a car with a fancy GPS system – if the navigation stops working, you can still drive the car, but you lose all those convenient features that made you choose that model in the first place. The complexity of smart appliance systems means there are more potential points of failure compared to traditional appliances. Your smart refrigerator might have a perfectly functioning compressor and cooling system, but if its internal computer crashes, you could lose access to temperature controls, energy monitoring, and inventory tracking features. Similarly, a smart dishwasher might clean dishes beautifully while its Wi-Fi connectivity remains completely non-functional. Understanding this distinction helps homeowners prioritize which issues need immediate professional attention versus those that can wait for a convenient repair appointment. Most smart appliance failures occur at the software level rather than in the mechanical components. This is actually good news for homeowners because software issues are often easier and less expensive to resolve than mechanical breakdowns. However, it also means that troubleshooting requires a different approach than you might use with traditional appliances. Instead of checking for loose connections or worn parts, you’ll need to think about network settings, app compatibility, and firmware versions.
Smart appliances are essentially traditional household devices equipped with sensors, processors, and internet connectivity that allow them to communicate with your smartphone, voice assistants, and other connected devices. When these high-tech features malfunction, it’s usually because one of these technological components has encountered a problem rather than the core appliance function failing. Think of it like a car with a fancy GPS system – if the navigation stops working, you can still drive the car, but you lose all those convenient features that made you choose that model in the first place. The complexity of smart appliance systems means there are more potential points of failure compared to traditional appliances. Your smart refrigerator might have a perfectly functioning compressor and cooling system, but if its internal computer crashes, you could lose access to temperature controls, energy monitoring, and inventory tracking features. Similarly, a smart dishwasher might clean dishes beautifully while its Wi-Fi connectivity remains completely non-functional. Understanding this distinction helps homeowners prioritize which issues need immediate professional attention versus those that can wait for a convenient repair appointment. Most smart appliance failures occur at the software level rather than in the mechanical components. This is actually good news for homeowners because software issues are often easier and less expensive to resolve than mechanical breakdowns. However, it also means that troubleshooting requires a different approach than you might use with traditional appliances. Instead of checking for loose connections or worn parts, you’ll need to think about network settings, app compatibility, and firmware versions.
Wi-Fi Connectivity and Network Issues
The foundation of any smart appliance’s advanced features relies on a stable internet connection, making Wi-Fi problems the most common culprit when high-tech features stop working. When your smart devices can’t communicate with your home network, they essentially become expensive versions of their traditional counterparts. This connectivity dependence means that even minor changes to your home network setup can cause widespread issues across multiple appliances simultaneously. 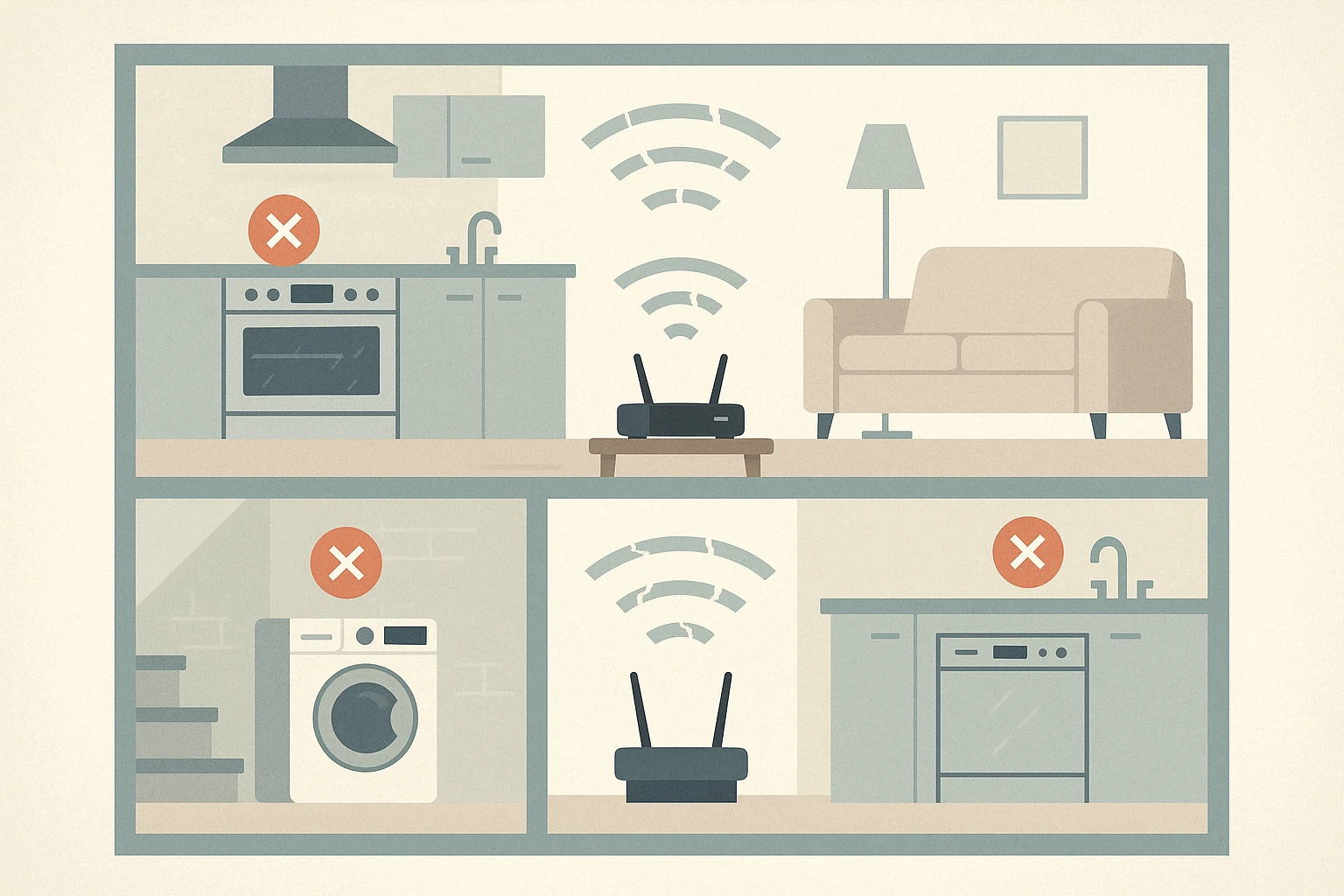 Router placement plays a crucial role in smart appliance performance, especially in larger homes or spaces with thick walls that can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Many homeowners don’t realize that appliances installed in basements, garages, or far corners of the house may struggle to maintain consistent connectivity even when other devices in the same area work fine. Smart appliances often require more stable connections than smartphones or tablets because they need to maintain constant communication for features like remote monitoring and automatic updates. Network congestion becomes particularly problematic in homes with multiple smart devices competing for bandwidth. When your internet service provider experiences slowdowns or when numerous devices are streaming video content simultaneously, smart appliances may disconnect or experience delayed responses. This issue has become more common as households add more connected devices, from smart thermostats to security cameras, all sharing the same network resources. Password changes and network security updates frequently cause smart appliances to lose connectivity without homeowners realizing the connection. Unlike phones or computers that prompt users to re-enter network credentials, many smart appliances simply stop working when authentication fails. This silent failure mode means appliances can appear broken when they actually just need to be reconnected to the updated network settings. Internet service provider changes or equipment upgrades can also disrupt smart appliance functionality in unexpected ways. New routers may use different frequency bands or security protocols that aren’t compatible with older smart appliances. Some devices only connect to 2.4GHz networks, while newer routers might prioritize 5GHz bands, creating compatibility conflicts that prevent successful connections.
Router placement plays a crucial role in smart appliance performance, especially in larger homes or spaces with thick walls that can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Many homeowners don’t realize that appliances installed in basements, garages, or far corners of the house may struggle to maintain consistent connectivity even when other devices in the same area work fine. Smart appliances often require more stable connections than smartphones or tablets because they need to maintain constant communication for features like remote monitoring and automatic updates. Network congestion becomes particularly problematic in homes with multiple smart devices competing for bandwidth. When your internet service provider experiences slowdowns or when numerous devices are streaming video content simultaneously, smart appliances may disconnect or experience delayed responses. This issue has become more common as households add more connected devices, from smart thermostats to security cameras, all sharing the same network resources. Password changes and network security updates frequently cause smart appliances to lose connectivity without homeowners realizing the connection. Unlike phones or computers that prompt users to re-enter network credentials, many smart appliances simply stop working when authentication fails. This silent failure mode means appliances can appear broken when they actually just need to be reconnected to the updated network settings. Internet service provider changes or equipment upgrades can also disrupt smart appliance functionality in unexpected ways. New routers may use different frequency bands or security protocols that aren’t compatible with older smart appliances. Some devices only connect to 2.4GHz networks, while newer routers might prioritize 5GHz bands, creating compatibility conflicts that prevent successful connections.
Software Updates and Firmware Problems
Moving from connectivity issues to the software that powers these smart features, firmware problems represent another major category of smart appliance failures that can leave homeowners frustrated and confused. Just like smartphones and computers, smart appliances rely on complex software systems that require regular updates to function properly, maintain security, and access new features. However, unlike personal devices that typically update automatically and obviously, appliance firmware updates often happen behind the scenes or require manual intervention that many users overlook. Firmware corruption can occur during power outages, network interruptions, or failed update attempts, leaving appliances in an unstable state where some features work while others don’t. This partial functionality can be particularly confusing because the appliance appears to be working normally for basic operations while advanced smart features remain non-functional. For example, a smart oven might heat and cook food perfectly but lose the ability to connect to mobile apps or respond to voice commands after a corrupted firmware update. Compatibility issues between different software versions create another common problem in smart appliance troubleshooting. Your appliance’s firmware might be outdated compared to the manufacturer’s mobile app, or conversely, an app update might introduce features that your appliance’s current firmware doesn’t support. These version mismatches can cause communication errors, feature limitations, or complete loss of smart functionality until all components are synchronized to compatible versions. Manufacturer support for older smart appliances varies significantly, with some companies providing regular updates for several years while others discontinue software support relatively quickly. When manufacturers stop releasing firmware updates, appliances may gradually lose compatibility with evolving smart home ecosystems, updated mobile operating systems, or new security protocols. This planned obsolescence affects smart appliances differently than traditional ones because the smart features become progressively less functional even when the core appliance mechanisms remain perfectly operational. Factory reset requirements sometimes become necessary when firmware problems are too complex for simple troubleshooting steps to resolve. However, performing a factory reset on a smart appliance typically means losing all custom settings, learned preferences, and connected device relationships. This reset process can be time-consuming to reverse, requiring homeowners to reconfigure network connections, reinstall mobile apps, and reprogram all their preferred settings and schedules.
Mobile App Integration Failures
Building on the complexity of firmware management, mobile app integration represents the user-facing side of smart appliance technology where many homeowners first notice problems with their high-tech features. The relationship between your smartphone and smart appliances creates multiple potential failure points, from app crashes and login problems to device recognition issues and sync failures. Because most people interact with their smart appliances primarily through mobile apps, problems in this area can make perfectly functional appliances seem completely broken. App store policies and mobile operating system updates frequently disrupt smart appliance functionality in ways that manufacturers struggle to predict or prevent. When Apple releases a new iOS version or Google updates Android system requirements, smart appliance apps may become incompatible overnight, leaving users unable to access their device controls. These compatibility breaks often require weeks or months for appliance manufacturers to release updated apps that work with new mobile operating systems. Account authentication problems plague many smart appliance users, especially those who upgrade phones, change email addresses, or modify passwords without properly updating their appliance app settings. Unlike traditional appliances that work independently, smart devices require constant verification of user credentials to maintain security and prevent unauthorized access. When authentication fails, appliances may lock users out of advanced features while continuing to operate in basic mode. Cloud service dependencies mean that smart appliance apps rely on external servers to facilitate communication between your phone and your appliances. When manufacturers experience server outages, undergo maintenance, or discontinue cloud services, all connected appliances lose their smart functionality simultaneously. These service interruptions can last hours or days, and in some cases, discontinued cloud services render smart features permanently inoperable. Multiple device management becomes increasingly complex as households add more smart appliances from different manufacturers, each requiring separate apps with unique interfaces and account systems. Users often struggle to remember which app controls which appliance, leading to confusion and frustration when troubleshooting problems. Additionally, managing multiple accounts, passwords, and app updates across numerous appliance brands creates opportunities for synchronization problems and access issues. Permission settings on mobile devices can inadvertently block smart appliance apps from accessing necessary system resources like location services, notifications, or network connectivity. Modern smartphones implement strict privacy controls that may prevent appliance apps from functioning properly if users accidentally deny critical permissions during initial setup or subsequent updates. These permission conflicts can cause partial app functionality where some features work while others remain inaccessible.
Voice Assistant and Smart Home Hub Connectivity
Expanding beyond individual app interactions, voice assistant integration represents one of the most convenient yet problematic aspects of modern smart appliance management, where multiple systems must work together seamlessly to provide hands-free control. When homeowners can’t adjust their smart thermostat by talking to Alexa or ask Google to preheat the oven, the problem often lies in the complex web of connections between voice assistants, smart home hubs, and individual appliances rather than in the appliances themselves. Smart home ecosystems require precise coordination between different manufacturers’ products, creating compatibility challenges that didn’t exist with traditional appliances that operated independently. Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Apple HomeKit, and Samsung SmartThings each use different communication protocols and security requirements, meaning that an appliance working perfectly with one system might not function at all with another. This fragmentation forces homeowners to carefully research compatibility before purchasing new smart appliances or risk discovering that their devices can’t communicate with their existing smart home setup. Hub connectivity problems frequently occur when smart home systems lose track of connected devices after power outages, network changes, or system updates. Unlike direct Wi-Fi connections between phones and appliances, hub-based systems create an additional layer of potential failure points where communication can break down. When hubs lose connection to appliances, voice commands fail even though the appliances remain connected to the home network and controllable through their dedicated mobile apps. Device discovery and pairing processes often confuse homeowners who expect smart appliances to connect automatically to voice assistants like smartphones connect to Bluetooth devices. However, smart home integration typically requires manual setup procedures involving specific voice commands, app configurations, and account linking steps that vary significantly between different manufacturers and platforms. Incomplete or incorrect setup procedures result in partial functionality where some voice commands work while others don’t respond at all. Skill and integration updates for voice assistants can unexpectedly break existing smart appliance connections when manufacturers modify their communication protocols or when voice assistant platforms change their requirements. Homeowners may discover that appliances that responded perfectly to voice commands suddenly stop working after automatic updates, requiring manual reconfiguration or skill reinstallation to restore functionality. These disruptions often occur without clear notification to users, leading to confusion about why previously working features have stopped responding. Command recognition accuracy varies significantly between different smart appliance types and manufacturers, with some devices responding reliably to voice instructions while others require very specific phrasing or multiple attempts to execute commands correctly. This inconsistency can make smart home voice control feel unreliable even when all technical connections are working properly, leading homeowners to abandon voice features in favor of manual app control or traditional physical controls.
Sensor and Display Malfunctions
Transitioning from communication problems to hardware-related issues, sensor and display malfunctions represent a category of smart appliance problems that often require professional diagnosis and repair rather than simple troubleshooting steps. These components serve as the eyes and interface of smart appliances, collecting data about operating conditions and presenting information to users through touchscreens, LED displays, and indicator lights. Touchscreen responsiveness problems affect many smart appliances that rely on display interfaces for user interaction and settings management. Unlike smartphone screens that users handle carefully, appliance touchscreens endure kitchen environments with temperature fluctuations, humidity, cooking vapors, and frequent cleaning with potentially harsh chemicals. These conditions can degrade screen sensitivity over time, cause dead zones where touches aren’t recognized, or create phantom touches that register inputs when no one is interacting with the display. Temperature and humidity sensors play crucial roles in smart appliance operation, but they’re also vulnerable to calibration drift, dust accumulation, and damage from cleaning procedures. When these sensors provide inaccurate readings, smart appliances may behave erratically, such as refrigerators that can’t maintain proper temperatures, ovens that don’t preheat correctly, or dishwashers that run inappropriate wash cycles. Sensor problems often develop gradually, making them difficult to notice until appliance performance becomes obviously problematic. Display backlighting failures can render smart appliance interfaces partially or completely unreadable while leaving the underlying functionality intact. These lighting problems may manifest as dim screens, flickering displays, or complete blackouts that make it impossible to access smart features through the appliance’s built-in interface. While mobile apps may still provide some control capability, display failures significantly impact user experience and may indicate developing electrical problems that require professional attention. Proximity and motion sensors integrated into modern smart appliances can malfunction due to dust buildup, physical damage, or electrical interference from other devices. When these sensors fail, appliances may not activate automatically when approached, may not detect when doors are opened or closed, or may not respond to gesture controls as designed. These sensor failures often require specialized diagnostic equipment to identify and resolve properly. Environmental interference from other electronic devices can disrupt sensor accuracy in smart appliances, particularly in kitchens with multiple connected devices operating simultaneously. Microwave ovens, induction cooktops, and wireless routers can generate electromagnetic interference that affects sensitive sensors, causing inconsistent readings or temporary malfunctions that appear and disappear unpredictably.
Power and Electrical System Issues
Behind all the sophisticated technology in smart appliances lies the fundamental requirement for stable electrical power, making power-related problems a critical category that can disable both smart features and basic appliance functions simultaneously. Unlike traditional appliances that typically require only consistent voltage and amperage, smart appliances need clean, stable power to support their sensitive electronic components, wireless communication systems, and data processing capabilities. Power surge damage represents a significant threat to smart appliances because their electronic components are more vulnerable to voltage spikes than the simple motors and heating elements found in traditional appliances. Even minor electrical disturbances that wouldn’t affect conventional devices can corrupt memory, damage processors, or disrupt communication circuits in smart appliances. This vulnerability means that homes without adequate surge protection may experience repeated smart appliance failures during storms or when electrical grid problems occur. Electrical wiring issues in older homes can prevent smart appliances from receiving the consistent power quality they require for reliable operation. Problems like loose connections, inadequate grounding, or voltage fluctuations may cause smart features to malfunction intermittently while basic appliance functions continue working normally. These electrical problems often require professional diagnosis because they can be difficult to distinguish from software or connectivity issues without proper testing equipment. Power management systems within smart appliances can fail independently of the main appliance functions, creating situations where devices work normally for basic operations but lose all smart capabilities. These internal power supply problems might affect only the wireless communication modules, display systems, or processing units while leaving motors, heating elements, and other primary components fully functional. Diagnosing these selective power failures typically requires specialized knowledge of appliance electrical systems. Brownout conditions, where electrical voltage drops below normal levels without complete power loss, can cause smart appliances to behave erratically or enter protective modes that disable advanced features. Unlike complete power outages that clearly indicate electrical problems, brownouts may not be obvious to homeowners while still causing significant disruption to sensitive electronic systems. Smart appliances experiencing brownout conditions may restart repeatedly, lose network connections, or display error messages that seem unrelated to power issues. Ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) sensitivity in smart appliances can cause nuisance tripping that appears to be appliance malfunctions when the actual problem lies in electrical installation or moisture detection systems. Modern smart appliances often include more sophisticated electrical monitoring than traditional devices, making them more likely to trigger GFCI protection even when no actual safety hazard exists. These false trips can frustrate homeowners who don’t understand why their appliances keep shutting off seemingly randomly.
Professional Diagnosis and Repair Considerations
When basic troubleshooting steps fail to resolve smart appliance problems, understanding when and how to seek professional help becomes crucial for homeowners who want to avoid unnecessary expenses while ensuring their appliances receive proper care. The decision between DIY troubleshooting and professional intervention depends on the complexity of the problem, the potential risks involved, and the specific expertise required to diagnose and repair modern smart appliance systems.  Warranty considerations play a significant role in professional repair decisions because many smart appliance manufacturers void warranties when unauthorized technicians attempt repairs or when homeowners modify software settings beyond basic user controls. Professional repair services authorized by manufacturers can perform warranty work while maintaining coverage for future problems, making them a safer choice for newer appliances even when repair costs seem higher than independent alternatives. Diagnostic capabilities of professional appliance repair services have evolved to include specialized tools and software for testing smart appliance systems that aren’t available to general consumers. Professional technicians can access manufacturer diagnostic modes, update firmware directly, test sensor accuracy, and analyze communication logs to identify problems that would be impossible to detect through basic troubleshooting. These advanced diagnostic capabilities often make the difference between successful repairs and expensive component replacements. Cost-benefit analysis for smart appliance repairs requires considering not only the immediate repair expense but also the ongoing value of smart features compared to replacing the appliance with a traditional model. Professional technicians can provide accurate assessments of repair costs and expected longevity, helping homeowners make informed decisions about whether investing in smart appliance repairs makes financial sense compared to replacement options. Specialized training requirements for smart appliance repair mean that not all appliance technicians are qualified to work on connected devices with complex software and networking components. Homeowners should verify that repair services have specific experience with smart appliances and current training on the brands and models they own. General appliance repair experience doesn’t automatically translate to competence with smart technology troubleshooting and repair. Service documentation and follow-up support from professional repair companies can provide valuable assistance for preventing future problems and optimizing smart appliance performance. Quality repair services typically provide detailed explanations of problems found, recommendations for preventing similar issues, and ongoing support for questions about appliance operation and maintenance.
Warranty considerations play a significant role in professional repair decisions because many smart appliance manufacturers void warranties when unauthorized technicians attempt repairs or when homeowners modify software settings beyond basic user controls. Professional repair services authorized by manufacturers can perform warranty work while maintaining coverage for future problems, making them a safer choice for newer appliances even when repair costs seem higher than independent alternatives. Diagnostic capabilities of professional appliance repair services have evolved to include specialized tools and software for testing smart appliance systems that aren’t available to general consumers. Professional technicians can access manufacturer diagnostic modes, update firmware directly, test sensor accuracy, and analyze communication logs to identify problems that would be impossible to detect through basic troubleshooting. These advanced diagnostic capabilities often make the difference between successful repairs and expensive component replacements. Cost-benefit analysis for smart appliance repairs requires considering not only the immediate repair expense but also the ongoing value of smart features compared to replacing the appliance with a traditional model. Professional technicians can provide accurate assessments of repair costs and expected longevity, helping homeowners make informed decisions about whether investing in smart appliance repairs makes financial sense compared to replacement options. Specialized training requirements for smart appliance repair mean that not all appliance technicians are qualified to work on connected devices with complex software and networking components. Homeowners should verify that repair services have specific experience with smart appliances and current training on the brands and models they own. General appliance repair experience doesn’t automatically translate to competence with smart technology troubleshooting and repair. Service documentation and follow-up support from professional repair companies can provide valuable assistance for preventing future problems and optimizing smart appliance performance. Quality repair services typically provide detailed explanations of problems found, recommendations for preventing similar issues, and ongoing support for questions about appliance operation and maintenance.
Frequently Asked questions
Why does my smart appliance keep disconnecting from Wi-Fi?
Smart appliances typically disconnect from Wi-Fi due to weak signal strength, network congestion, or router compatibility issues. The most common cause is insufficient signal strength in the appliance’s location, especially for devices installed in basements, garages, or areas far from your router. Network congestion occurs when too many devices compete for bandwidth simultaneously, causing smart appliances to drop connections during peak usage periods. Router compatibility problems arise when older appliances can’t connect to newer routers that use different frequency bands or security protocols. To resolve persistent disconnection issues, try moving your router closer to the appliance or installing a Wi-Fi extender to boost signal strength. Check if your router broadcasts both 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks, as many smart appliances only connect to 2.4GHz bands. Consider upgrading your internet plan if multiple devices regularly experience connectivity problems, and ensure your router firmware stays updated to maintain compatibility with connected appliances.
How do I know if my smart appliance needs a firmware update?
Most smart appliances indicate firmware update availability through their mobile apps, display screens, or manufacturer notifications, but the process varies significantly between brands and models. Check your appliance’s mobile app regularly for update notifications, as manufacturers typically push notifications through their dedicated applications when new firmware becomes available. Many appliances also display update prompts on their built-in screens or through LED indicator patterns that signal available updates. You can manually check for firmware updates by accessing your appliance’s settings menu through its mobile app or built-in display interface. Most manufacturers also maintain support websites where you can enter your model number to check current firmware versions and download updates if needed. If your appliance’s smart features have stopped working recently or you’re experiencing connectivity problems, checking for firmware updates should be one of your first troubleshooting steps.
What should I do when my smart appliance’s app won’t connect to the device?
App connection failures typically result from authentication problems, outdated software, or network connectivity issues that require systematic troubleshooting to identify and resolve. Start by ensuring both your mobile device and the appliance are connected to the same Wi–Fi network, as many apps require devices to share the same network for initial setup and ongoing communication. Check that your smartphone’s app is updated to the latest version available in your device’s app store, as outdated apps frequently lose compatibility with appliance firmware. If network and app updates don’t resolve the connection problem, try logging out of your appliance account completely and logging back in with your current credentials. Clear the app’s cache and data through your phone’s settings menu, then restart both your phone and the appliance before attempting to reconnect. For persistent connection problems, delete and reinstall the appliance app entirely, as corrupted app data can prevent successful device communication even when all other systems are working properly.
Why won’t my voice assistant recognize commands for my smart appliances?
Voice assistant recognition problems often stem from incomplete device setup, skill configuration errors, or changes in account linking that disconnect appliances from voice control systems. Verify that your smart appliances are properly linked to your voice assistant account by checking the device list in your assistant’s mobile app and ensuring all appliances appear as connected and responsive. Many voice assistants require specific skills or integrations to be enabled for different appliance brands, so confirm that necessary skills are installed and activated for your devices. Command phrasing plays a crucial role in voice assistant recognition, as different appliances respond to different voice patterns and keywords. Try using the exact command phrases recommended in your appliance’s documentation or voice assistant skill description, as slight variations in wording can prevent recognition. If commands worked previously but stopped responding recently, check for skill updates or account linking changes that may require reconfiguration to restore functionality.
Wrapping Up
Smart appliance troubleshooting doesn’t have to feel like solving a complex puzzle when you understand the common patterns behind most high-tech feature failures. The majority of problems stem from connectivity issues, software conflicts, or power-related disruptions rather than actual mechanical breakdowns, which means many solutions are within reach of determined homeowners armed with the right knowledge. By systematically working through Wi-Fi connections, firmware updates, app configurations, and basic power cycling procedures, you can resolve most smart appliance glitches without requiring expensive professional service calls. Remember that smart appliances are essentially computers with household functions attached, so approaching problems with that mindset helps prioritize troubleshooting steps and set realistic expectations for repair timelines. When basic troubleshooting doesn’t restore functionality, professional repair services specializing in smart appliance technology can provide the specialized diagnostic tools and expertise needed to identify complex problems that aren’t immediately obvious to homeowners. The key to maintaining reliable smart appliance performance lies in proactive maintenance of your home network infrastructure, regular software updates, and understanding the interconnected nature of modern connected devices. Don’t let temporary technical glitches discourage you from enjoying the convenience and efficiency benefits that smart appliances provide when they’re working properly. With patience and systematic troubleshooting, most smart appliance problems can be resolved, restoring those helpful features that make daily household management more convenient and efficient.
